Showing posts with label principles. Show all posts
Showing posts with label principles. Show all posts
Saturday, August 14, 2010
A Model of an Athlete, of Athletecisim: z-health's 9s - also a model of coaching
Follow @mcphoo
Tweet
Here's a question that seems to be poking me on from the earlier "do we enjoy all our workouts/practices/training sessions?" And it's: What is our model of performance? what are the qualities to which we aspire in terms of living what i'm increasingly seeing as "embodied" lives - where we get that we're not just brains with bodies, but that our bodies are life enhancing? Before answering this, one might wonder why do we need a model? Why not just you know, keep moving? Eat well, rest well, move well.
Yup. That's great. For a certain quality of well. But what makes up that "wellness"? How do we understand that wellness so we can make decisions about what to include in our practice and what to discard; what's useful and what's for later, or not at all? Frameworks, models of a system, an organism can help. Indeed, these kinds of templates are usually more effective than specific programs. They usually relate to principles from which skills and pragmatics can be derived, progress or just needs assessed. And if we're actually in a place to coach someone, the value of such frameworks becomes even greater.
Let's consider what we mean by principle centered frameworks, consider the athlete in this, and take a look at the benefit of such an approach as a coaching model, too.
Principle Informed Frameworks - Models in Other Domains
 We have examples of such adaptable models in other aspects of our way of being in the world. Steven Covey, author of the ubiquitously cited 7 Habits of Highly Effective People
We have examples of such adaptable models in other aspects of our way of being in the world. Steven Covey, author of the ubiquitously cited 7 Habits of Highly Effective People demonstrates why
demonstrates why having a framework informing what we do is part of being truly effective. For instance, he's well known for his expression rather than prioritise your schedule "schedule your priorities." In other words, make deliberate time for what is important. That's a principle. He calls it "put first things first" or suggests that "the main thing is to keep the main thing the main thing." To figure out what comes first, he has strategies to align with one's "true north" - one's principles. Come from principles first, not strategies like to-do lists or calendars. Those are tools; they are just the implementation details.
having a framework informing what we do is part of being truly effective. For instance, he's well known for his expression rather than prioritise your schedule "schedule your priorities." In other words, make deliberate time for what is important. That's a principle. He calls it "put first things first" or suggests that "the main thing is to keep the main thing the main thing." To figure out what comes first, he has strategies to align with one's "true north" - one's principles. Come from principles first, not strategies like to-do lists or calendars. Those are tools; they are just the implementation details.


 In another now-foundational text about business success, Jim Collins and his team in Good to Great
In another now-foundational text about business success, Jim Collins and his team in Good to Great  attempt to reverse engineer a set of principles that are in common with companies that made the leap from being Good companies to Great companies - companies that have beaten the market repeatedly for a particular period, by a particular percentage consecutively.
attempt to reverse engineer a set of principles that are in common with companies that made the leap from being Good companies to Great companies - companies that have beaten the market repeatedly for a particular period, by a particular percentage consecutively.
Themes recur from attitudes of leaders to the way organizational management works. One of my favorite principles from the book is Get the Right People on the Bus. With the right folks, one can do almost anything, and thrive in any climate.
 What's also interesting about the book is how many times Collins finds himself asking participants in the interviews about what their company's mission or vision is - and how this wasn't necessarily ever an explicit thing for people. The actions they took were not necesarily part of a pre-fabricated plan. It was just the right thing to do.
What's also interesting about the book is how many times Collins finds himself asking participants in the interviews about what their company's mission or vision is - and how this wasn't necessarily ever an explicit thing for people. The actions they took were not necesarily part of a pre-fabricated plan. It was just the right thing to do.
The role of folks like Covey and Collins is to analyse the seeming instinctive behaviours of the Great and translate them into principles first and, following this, skills that can be practiced in line with these principles. For Covey, i'd suggest that the book First Things First
and translate them into principles first and, following this, skills that can be practiced in line with these principles. For Covey, i'd suggest that the book First Things First  is very much the workbook for the temporal organization part of the Seven Habits.
is very much the workbook for the temporal organization part of the Seven Habits.
By developing skills practice, as in anything, skills are first paths towards accessing an action we want to accomplish - from a better tennis swing to a better email response practice (which may mean less email). Second, the repeated practice of a skill makes it a kind of habit or even reflex. That is we do it without having to think about it. It becomes engrained. For folks who constantly practice their skills, they become not just reflexive habits but stronger patterns. Talking with Steve Cotter the other day about a really nice GS snatch tutorial video he did, he was saying he had to do a new one because he was finding his technique was refining much faster now - months rather than years. Steve has been so focussed on his snatch technique and on teaching that technique in his IKFF for GS practice and competition, no kidding he's finding new performance refinements fast. It's amazing what having to teach does to thinking about breaking something into the most teachable units.
Model of the Athlete means Focus for Skills Development
Which brings us back to athletics from a principle driven model. So what is an athlete? or what are the attributes of athleticism? That's almost as bad as asking "what is motivation?" It's a skill too.
SO here's a model of an athlete that Eric Cobb put together and around which Z-Health (overview and index of related articles) is based.
Strength, sustenance, skill, suppleness, stamina, structure, spirit, style and speed. All *equal sized* nodes on this graph. We all need strength: what kind of strength do we need in particular for what we do? Likewise suppleness. We all need to eat and recover. How tune that? How might one's structure be utilized or tuned to better support one's athletic goals? What about sports skills? How's one's physiological stamina mapped to one's ability to endure, to support, to be? to one's spirit? And what about one's own way of doing things, one's style? How support that to enhance rather than break one?
In graphing terms, this equal-node model is also a hub and spoke diagram where "the athlete is at the center" (the phrase you will here Cobb and Co. repeat often) and where everything is mediated through that center. This paradigm of the athlete as the mediating center of some core attributes takes coaching in an interesting direction, and situates Z-Health as a robust approach to training longevity that goes way beyond the foundation of movement drills.
I've written quite a bit about the principles from neuroscience that Z-Health translates as a kind of engineering of movement science or neuroscience into training practice. We've looked at Z-Health from dynamic joint mobility, to pain models, to threat modulation to CNS testing. the focus has been to improve movement quality and thereby to improve movement performance. These are the fundamental components of Z-Health. Moving limbs well, threat modulation for effective adapatation, these are the primary building blocks of the Z-Health approach as taught in the R,I,S and T certifications. But these fundamentals are themselves motivated by this overall model of the athlete, where the goal is how best support the athlete.
In other words, the goal of Z-Health as an approach is actually to use this model of the athlete (and in Z the starting point is "everyone is an athlete") as a principle-oriented, skills-based guide to coaching> The goal, as a coach, is to learn the skills - driven by the best practical, clinical and science lead research out there - to guide an athlete's performance on each of these parameters. Cobb talks about the best coaching is knowing when to emphasize which of these compnents in training, which then means knowing how emphasize the component, and within that, what content specifically to offer the athlete. That's non-trivial. That's serious stuff. Principles are serious. And the expectation is rather that as coaches we walk the walk not just talk the talk. I've said it before: everyone needs a coach. Do you have a coach who can talk with you about your speed and your swing and your sustenance? Why not? Here's a list of master trainers who really walk the walk.
Great Coaching - Practical Principled Coaching
for Deliverable, Repeatable, Skills-based Athleticism
We are wired to learn and to adapt - it's part of our survival mechanism.
Part of the approach of the 9S model is to break down components of practice into learnable skills. All of the movements in the basic drills of R and I phase are based on athletic movements (this is particularly apparent in I-Phase).
In the 9S courses, the emphasis is on getting at these larger components of athleticism and focusing on usable knowledge and practical skills, from nutrition to strength to speed to style, to make us better coaches, so that we have the depth and breadth to provide the right knowledge, the right tools, at the right time, within a pretty broad, holistic view of an athlete fundamentally as a person. As an example, last year in Sustenance and Spirit, we spent considerable time practicing coaching skills as drills. Active Listening anyone? This was really challenging work for a lot of us: how to listen and respond rather than just program and push. That was aside from the depth of detail we got into on basic nutrition, inflammation processes, supplement studies and related. Not just knowledge; not just tools but how to engage, when to deliver the right ones and the right time.

 The cool thing i think is that stuff when we see someone great do it, we often take the approach of "wow, that person is really gifted - they just have that talent. what a gift" But a lot of that stuff can be taught. And practiced. With intent. We can develop skills. We can learn not only the tools to have to be a great coach, but how to BE a great coach.
The cool thing i think is that stuff when we see someone great do it, we often take the approach of "wow, that person is really gifted - they just have that talent. what a gift" But a lot of that stuff can be taught. And practiced. With intent. We can develop skills. We can learn not only the tools to have to be a great coach, but how to BE a great coach.
And sure there may be folks who are naturally gifted. But as Geoff Colvin notes in Talent is Overrated , and as Gladwell notes in Outliers
, and as Gladwell notes in Outliers , putting in the time to practice a skill is what separates the best from the rest. We need our ten thousand reps. But knowing the skills to rep, when, for how long - that's what makes a great coach, and how to be a great coach is no small thing. But a lot of it is skills too, and skills can be (a) taught and (b) practiced.
, putting in the time to practice a skill is what separates the best from the rest. We need our ten thousand reps. But knowing the skills to rep, when, for how long - that's what makes a great coach, and how to be a great coach is no small thing. But a lot of it is skills too, and skills can be (a) taught and (b) practiced.
There's an elegance to Cobb's model that i suspect as it becomes better known will end up plastered over strength coaches' walls. Sports programs will teach the 9S's as a way of communicating training goals and measurements. And what a day that will be.
It takes a certain kind of genius to ask the obvious questions and then find not only the non-trivial answers but the solutions that make them tractable, teachable, learnable while letting them still be wonderful. I think that likely Eric Cobb has done this with this approach to coaching, with the athlete-centred model of athleticism. Why? because it is principle centered, science based and skills-oriented. Each course, each cert is always geared to "what can you do with this monday morning when you're back with your athletes?"
Taking It Home.
This post started with a question about how do we guide our pursuit of embodied happiness, embodied well being? Having a model of what makes up success in a given domain seems to be a pretty good approach. Covey has such a model for engaging with others. Collins has a model for corporate progress. And i'd suggest Cobb (wow, another C) has a model for athletic well being. And since we all have bodies and move, well, everyone is an athlete.
So if you've been riffing on Z-Health as a great approach to movement, and feeling better, maybe moving out of pain or into better performance having seen a Z-Health coach, that's great. It is super fantastic for this. If you're interested in getting started with Z-Health, here's a big fat Z-Health overview.

If you're thinking about an approach to training, about learning skills to train better, and about getting at the science of movement and these 9S's in an intelligent, useful and usable way, Z-Health is really reaching to get folks there. And that's kind of a new paradigm too for fitness, strength and conditioning, and sports-oriented training. Kinda makes me go hmm. This is an interesting place to be, and i'm inclined to watch this space. Tweet Follow @begin2dig
Yup. That's great. For a certain quality of well. But what makes up that "wellness"? How do we understand that wellness so we can make decisions about what to include in our practice and what to discard; what's useful and what's for later, or not at all? Frameworks, models of a system, an organism can help. Indeed, these kinds of templates are usually more effective than specific programs. They usually relate to principles from which skills and pragmatics can be derived, progress or just needs assessed. And if we're actually in a place to coach someone, the value of such frameworks becomes even greater.
Let's consider what we mean by principle centered frameworks, consider the athlete in this, and take a look at the benefit of such an approach as a coaching model, too.
Principle Informed Frameworks - Models in Other Domains
 We have examples of such adaptable models in other aspects of our way of being in the world. Steven Covey, author of the ubiquitously cited 7 Habits of Highly Effective People
We have examples of such adaptable models in other aspects of our way of being in the world. Steven Covey, author of the ubiquitously cited 7 Habits of Highly Effective People
Themes recur from attitudes of leaders to the way organizational management works. One of my favorite principles from the book is Get the Right People on the Bus. With the right folks, one can do almost anything, and thrive in any climate.
 What's also interesting about the book is how many times Collins finds himself asking participants in the interviews about what their company's mission or vision is - and how this wasn't necessarily ever an explicit thing for people. The actions they took were not necesarily part of a pre-fabricated plan. It was just the right thing to do.
What's also interesting about the book is how many times Collins finds himself asking participants in the interviews about what their company's mission or vision is - and how this wasn't necessarily ever an explicit thing for people. The actions they took were not necesarily part of a pre-fabricated plan. It was just the right thing to do.The role of folks like Covey and Collins is to analyse the seeming instinctive behaviours of the Great
By developing skills practice, as in anything, skills are first paths towards accessing an action we want to accomplish - from a better tennis swing to a better email response practice (which may mean less email). Second, the repeated practice of a skill makes it a kind of habit or even reflex. That is we do it without having to think about it. It becomes engrained. For folks who constantly practice their skills, they become not just reflexive habits but stronger patterns. Talking with Steve Cotter the other day about a really nice GS snatch tutorial video he did, he was saying he had to do a new one because he was finding his technique was refining much faster now - months rather than years. Steve has been so focussed on his snatch technique and on teaching that technique in his IKFF for GS practice and competition, no kidding he's finding new performance refinements fast. It's amazing what having to teach does to thinking about breaking something into the most teachable units.
Model of the Athlete means Focus for Skills Development
Which brings us back to athletics from a principle driven model. So what is an athlete? or what are the attributes of athleticism? That's almost as bad as asking "what is motivation?" It's a skill too.
SO here's a model of an athlete that Eric Cobb put together and around which Z-Health (overview and index of related articles) is based.
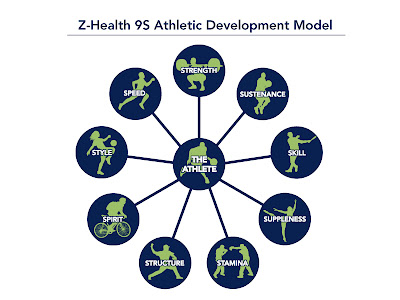 |
| The Z-Health 9S model of the Athlete |
Strength, sustenance, skill, suppleness, stamina, structure, spirit, style and speed. All *equal sized* nodes on this graph. We all need strength: what kind of strength do we need in particular for what we do? Likewise suppleness. We all need to eat and recover. How tune that? How might one's structure be utilized or tuned to better support one's athletic goals? What about sports skills? How's one's physiological stamina mapped to one's ability to endure, to support, to be? to one's spirit? And what about one's own way of doing things, one's style? How support that to enhance rather than break one?
In graphing terms, this equal-node model is also a hub and spoke diagram where "the athlete is at the center" (the phrase you will here Cobb and Co. repeat often) and where everything is mediated through that center. This paradigm of the athlete as the mediating center of some core attributes takes coaching in an interesting direction, and situates Z-Health as a robust approach to training longevity that goes way beyond the foundation of movement drills.
I've written quite a bit about the principles from neuroscience that Z-Health translates as a kind of engineering of movement science or neuroscience into training practice. We've looked at Z-Health from dynamic joint mobility, to pain models, to threat modulation to CNS testing. the focus has been to improve movement quality and thereby to improve movement performance. These are the fundamental components of Z-Health. Moving limbs well, threat modulation for effective adapatation, these are the primary building blocks of the Z-Health approach as taught in the R,I,S and T certifications. But these fundamentals are themselves motivated by this overall model of the athlete, where the goal is how best support the athlete.
In other words, the goal of Z-Health as an approach is actually to use this model of the athlete (and in Z the starting point is "everyone is an athlete") as a principle-oriented, skills-based guide to coaching> The goal, as a coach, is to learn the skills - driven by the best practical, clinical and science lead research out there - to guide an athlete's performance on each of these parameters. Cobb talks about the best coaching is knowing when to emphasize which of these compnents in training, which then means knowing how emphasize the component, and within that, what content specifically to offer the athlete. That's non-trivial. That's serious stuff. Principles are serious. And the expectation is rather that as coaches we walk the walk not just talk the talk. I've said it before: everyone needs a coach. Do you have a coach who can talk with you about your speed and your swing and your sustenance? Why not? Here's a list of master trainers who really walk the walk.
Great Coaching - Practical Principled Coaching
for Deliverable, Repeatable, Skills-based Athleticism
We are wired to learn and to adapt - it's part of our survival mechanism.
Part of the approach of the 9S model is to break down components of practice into learnable skills. All of the movements in the basic drills of R and I phase are based on athletic movements (this is particularly apparent in I-Phase).
In the 9S courses, the emphasis is on getting at these larger components of athleticism and focusing on usable knowledge and practical skills, from nutrition to strength to speed to style, to make us better coaches, so that we have the depth and breadth to provide the right knowledge, the right tools, at the right time, within a pretty broad, holistic view of an athlete fundamentally as a person. As an example, last year in Sustenance and Spirit, we spent considerable time practicing coaching skills as drills. Active Listening anyone? This was really challenging work for a lot of us: how to listen and respond rather than just program and push. That was aside from the depth of detail we got into on basic nutrition, inflammation processes, supplement studies and related. Not just knowledge; not just tools but how to engage, when to deliver the right ones and the right time.

And sure there may be folks who are naturally gifted. But as Geoff Colvin notes in Talent is Overrated
There's an elegance to Cobb's model that i suspect as it becomes better known will end up plastered over strength coaches' walls. Sports programs will teach the 9S's as a way of communicating training goals and measurements. And what a day that will be.
It takes a certain kind of genius to ask the obvious questions and then find not only the non-trivial answers but the solutions that make them tractable, teachable, learnable while letting them still be wonderful. I think that likely Eric Cobb has done this with this approach to coaching, with the athlete-centred model of athleticism. Why? because it is principle centered, science based and skills-oriented. Each course, each cert is always geared to "what can you do with this monday morning when you're back with your athletes?"
Taking It Home.
This post started with a question about how do we guide our pursuit of embodied happiness, embodied well being? Having a model of what makes up success in a given domain seems to be a pretty good approach. Covey has such a model for engaging with others. Collins has a model for corporate progress. And i'd suggest Cobb (wow, another C) has a model for athletic well being. And since we all have bodies and move, well, everyone is an athlete.
So if you've been riffing on Z-Health as a great approach to movement, and feeling better, maybe moving out of pain or into better performance having seen a Z-Health coach, that's great. It is super fantastic for this. If you're interested in getting started with Z-Health, here's a big fat Z-Health overview.

If you're thinking about an approach to training, about learning skills to train better, and about getting at the science of movement and these 9S's in an intelligent, useful and usable way, Z-Health is really reaching to get folks there. And that's kind of a new paradigm too for fitness, strength and conditioning, and sports-oriented training. Kinda makes me go hmm. This is an interesting place to be, and i'm inclined to watch this space. Tweet Follow @begin2dig
Labels:
9S,
coach,
principles,
z-health,
zhealth
Thursday, July 17, 2008
The Anti-Goal and First (things First) Principles
Follow @mcphoo
Tweet
Rannoch the Profound has a post about what happens to folks to scuttle their training:
Rannoch's observation got me wondering if one of the limiting factors that contributes to this OCD training effect is The Goal. This is not to say that goals are bad at all, but they can become mental mine fields when not treated appropriately. The voice in the head becomes:
That's kind of voice sounds irily reminiscent of procrastination/perfectionism. When the goal feels too daunting to achieve well, just leave it to the last minute and blame the fact that you didn't have enough time; or worry worry worry the little details (see "getting intrigued") rather than the big picture. Fear, fear of failure, of therefore being a failure is the thing in either case, and so inertia, it seems, sets in.
 Goals have a lot to answer for. In a sense, perhaps, as Stephen Covey might put it, it's a trust issue with ourselves: if we don't meet our commitment to our goals, we break faith with ourselves till we give up on ourselves. Frequently we may coat the cost of this failure by "getting intrigued" (described towards the end of this post on complexity ). Where we say oh this isn't right; that isn't right; i'll do it tomorrow when the moon and the stars are aligned and i feel better.
Goals have a lot to answer for. In a sense, perhaps, as Stephen Covey might put it, it's a trust issue with ourselves: if we don't meet our commitment to our goals, we break faith with ourselves till we give up on ourselves. Frequently we may coat the cost of this failure by "getting intrigued" (described towards the end of this post on complexity ). Where we say oh this isn't right; that isn't right; i'll do it tomorrow when the moon and the stars are aligned and i feel better.
For myself, this failure can be a particularly trying place to be if i can look back and see past successes, dedication, effort. So what's wrong with me *now* that that's not happening?
Maybe a better question to ask is what needs to be in place to re-establish relations with ourselves to feel that success of having done it than that dread of another day gone and the Goal further dishonored.
Maybe some of us who have already figured out that working out is important for our health, our spirit, our commitments, have to be to get to the headspace where the Real Goal is first to remember how to keep faith with ourselves and second to find a path back to doing that in terms of our fitness, health, well being. Perhaps it's as simple as re-setting the goal temporarily to something we KNOW we can accomplish, perhaps just to move something today. To move ourselves, a kettlebell, a rock - through space, perhaps multiple times in a row or throughout the day, and that that *is* a good thing, not only because it really *is* better than nothing, but because we said we would and we did.
Progressively, repeatedly, soon, the groove to that larger goal may just return, when we build our own confidence back up that we can keep our commitments to ourselves and we can trust ourselves with larger challenges.
In the interim, while simply keeping the commitment to move something in a day, we can give ourselves the space to figure out what may be acting in our lives right now such that we've been falling off the wagon; over complicating it, and what perhaps NOT to repeat once we get back in the groove such that we wind up back in the pit - if that's a recurring place to be.
A book i find helpful in this space is Stephen Covey's First Things First. The book talks about the importance of understanding why we *do* things, not in terms of some schedule like life as a perpetual to do list, but in order to define and move from principles. Don't prioritize your schedule; schedule your priorities is a phrase from the book. How do we determine our priorities? Based on what principles? what is our compass?
These questions apply here, in working out, too, i think. If we're not doing what we know to be right and good for our well being, and our ability to serve those we love, then something's askew, no?
Asking such questions can be a rather profound process. Covey suggests a number of ways to engage what can be very challenging work, where not working out is a symptom whose more profound causes may need investigation.
But in this meantime of engaging that process, and assuming that part of it may just be this loss of faith with ourselves to follow through on our commitments to ourselves, here's to everyone who's having a moment of doubt and self criticism. Let's give ourselves a break and all promise to do one push up, one swing, one pistol - one something - together in five minutes, and build on that.
Congratulations to us, we did it. Tweet Follow @begin2dig
You are trying get moving, not launch a rocket.
So many people seem to struggle with this. If the conditions aren't optimal they simply abort.
Give me 10 minutes and a kettlebell. Not so hard.
For those with workout OCD, it stops progress in it's tracks. The requirement to have everything in it's proper place prevents them from so much as breaking a sweat. This anabolic anxiety permeates everything they try to do. Plans are great but if you are fixated on a having all the ingredients for particular outcome you are missing "all that heavenly glory".
Rannoch's observation got me wondering if one of the limiting factors that contributes to this OCD training effect is The Goal. This is not to say that goals are bad at all, but they can become mental mine fields when not treated appropriately. The voice in the head becomes:
I *have* to do this kind of workout today because of this GOAL i have for date X, and if i can't train that way because of whatever (including just being pooped) then what's the point? anything "less" than the prescribed load, volume and moves is just failure (to serve teh goal), so why bother? I'm such a loser, aren't i?
That's kind of voice sounds irily reminiscent of procrastination/perfectionism. When the goal feels too daunting to achieve well, just leave it to the last minute and blame the fact that you didn't have enough time; or worry worry worry the little details (see "getting intrigued") rather than the big picture. Fear, fear of failure, of therefore being a failure is the thing in either case, and so inertia, it seems, sets in.
 Goals have a lot to answer for. In a sense, perhaps, as Stephen Covey might put it, it's a trust issue with ourselves: if we don't meet our commitment to our goals, we break faith with ourselves till we give up on ourselves. Frequently we may coat the cost of this failure by "getting intrigued" (described towards the end of this post on complexity ). Where we say oh this isn't right; that isn't right; i'll do it tomorrow when the moon and the stars are aligned and i feel better.
Goals have a lot to answer for. In a sense, perhaps, as Stephen Covey might put it, it's a trust issue with ourselves: if we don't meet our commitment to our goals, we break faith with ourselves till we give up on ourselves. Frequently we may coat the cost of this failure by "getting intrigued" (described towards the end of this post on complexity ). Where we say oh this isn't right; that isn't right; i'll do it tomorrow when the moon and the stars are aligned and i feel better. For myself, this failure can be a particularly trying place to be if i can look back and see past successes, dedication, effort. So what's wrong with me *now* that that's not happening?
Maybe a better question to ask is what needs to be in place to re-establish relations with ourselves to feel that success of having done it than that dread of another day gone and the Goal further dishonored.
Maybe some of us who have already figured out that working out is important for our health, our spirit, our commitments, have to be to get to the headspace where the Real Goal is first to remember how to keep faith with ourselves and second to find a path back to doing that in terms of our fitness, health, well being. Perhaps it's as simple as re-setting the goal temporarily to something we KNOW we can accomplish, perhaps just to move something today. To move ourselves, a kettlebell, a rock - through space, perhaps multiple times in a row or throughout the day, and that that *is* a good thing, not only because it really *is* better than nothing, but because we said we would and we did.
Progressively, repeatedly, soon, the groove to that larger goal may just return, when we build our own confidence back up that we can keep our commitments to ourselves and we can trust ourselves with larger challenges.
In the interim, while simply keeping the commitment to move something in a day, we can give ourselves the space to figure out what may be acting in our lives right now such that we've been falling off the wagon; over complicating it, and what perhaps NOT to repeat once we get back in the groove such that we wind up back in the pit - if that's a recurring place to be.
A book i find helpful in this space is Stephen Covey's First Things First. The book talks about the importance of understanding why we *do* things, not in terms of some schedule like life as a perpetual to do list, but in order to define and move from principles. Don't prioritize your schedule; schedule your priorities is a phrase from the book. How do we determine our priorities? Based on what principles? what is our compass?
These questions apply here, in working out, too, i think. If we're not doing what we know to be right and good for our well being, and our ability to serve those we love, then something's askew, no?
Asking such questions can be a rather profound process. Covey suggests a number of ways to engage what can be very challenging work, where not working out is a symptom whose more profound causes may need investigation.
But in this meantime of engaging that process, and assuming that part of it may just be this loss of faith with ourselves to follow through on our commitments to ourselves, here's to everyone who's having a moment of doubt and self criticism. Let's give ourselves a break and all promise to do one push up, one swing, one pistol - one something - together in five minutes, and build on that.
Congratulations to us, we did it. Tweet Follow @begin2dig
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)

 COACHING with dr. m.c.
COACHING with dr. m.c. 

